A Practical Guide to IoT Application Development
- Dec 15, 2025
- 16 min read
When you hear “IoT application development,” what probably comes to mind is the software that lets physical objects—from a smart thermostat in your home to a sensor on a factory floor—connect to the internet. You're not wrong, but it’s much deeper than that. You’re building the digital brain for a whole network of things, turning them from dumb objects into intelligent, interactive tools.
Unpacking the Layers of an IoT Solution

Real IoT application development isn't just about writing code for an app. It's about orchestrating a complex symphony where hardware and software have to work in perfect harmony.
Think about a smart home system. It’s not just the app on your phone. It’s an entire ecosystem: sensors, locks, lights, and cameras all talking to each other, to the cloud, and back to you. Each part has a very specific job, and if one fails, the whole experience breaks down.
To get a handle on this complexity, it helps to break down any IoT solution into four distinct layers. Each one builds on the last, turning raw, physical data into meaningful actions and insights for the user.
The growth here is staggering. By the end of 2023, there were already 16.6 billion connected IoT devices out in the wild. That number is expected to shoot past 29 billion by 2030. This isn't just a trend; it's a fundamental shift that demands scalable, resilient architectures capable of handling an absolute firehose of data. You can dig into more data on IoT device growth from recent studies.
An IoT application is the central nervous system for a network of connected objects. It allows them to sense their environment, communicate information, and perform actions, turning everyday items into smart, responsive tools.
Understanding these layers isn't just an academic exercise. For a CTO or engineering leader, this is your roadmap. It provides a clear framework for planning your product, allocating resources, and hiring the right talent.
Here’s a practical look at how these pieces fit together, using our smart home example.
The Four Core Layers of an IoT Solution
Any complete IoT solution, whether for a smart city or a connected vehicle, is built on these four foundational pillars. Each has its own set of technologies and engineering challenges.
Layer | Function | Key Technologies |
|---|---|---|
Device Layer (The Senses) | The physical hardware that gathers data from the world. | Sensors (temperature, motion, light), actuators (locks, motors), microcontrollers (Arduino, ESP32). |
Connectivity Layer (The Nerves) | Transmits data from the devices to the cloud. | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Cellular (LTE, 5G), LoRaWAN, MQTT, CoAP. |
Cloud Platform Layer (The Brain) | Processes, stores, and analyzes all incoming device data. | AWS IoT, Azure IoT Hub, Google Cloud IoT, Kafka, Kubernetes, databases (NoSQL, time-series). |
User Interface Layer (The Face) | The application the end-user interacts with to control and monitor devices. | Mobile apps (iOS/Android), web dashboards (React, Angular), voice interfaces (Alexa, Google Assistant). |
This structure makes it clear that you're not just building one thing; you're building four interconnected systems. Getting it right requires a team with expertise across this entire stack.
From the embedded firmware on the device to the machine learning models in the cloud and the slick UI on a phone, building a world-class IoT system requires elite engineering talent. TekRecruiter connects innovative companies with the top 1% of engineers globally, helping you assemble the perfect team to bring your connected vision to life.
Designing a Future-Proof IoT Architecture

A brilliant IoT concept can easily become a technical nightmare without the right architectural foundation. The decisions you make before writing a single line of code will determine if your app can scale reliably, run efficiently, and adapt down the road. This is a make-or-break step in IoT application development.
This isn't just about picking servers or databases; it's about drawing a blueprint for resilience and growth. A system that works fine with a hundred devices will absolutely crumble under the weight of ten thousand, forcing costly redesigns and handing the market to your competitors.
Monolithic vs Microservices Architectures
One of the first forks in the road is choosing between a monolithic or microservices architecture. Traditional monolithic systems lump all functions into one tightly-coupled application, but that approach is usually far too rigid for the dynamic world of IoT.
Think of a monolithic app like a house where the kitchen, bedroom, and plumbing are all part of one massive, indivisible structure. If the plumbing fails, the whole house might be unusable. In the same way, updating one tiny feature means you have to redeploy the entire application, risking system-wide chaos.
In contrast, a microservices architecture is like building with LEGOs. It breaks the application into a collection of small, independent services. Each service handles a specific job—like device authentication, data ingestion, or user notifications—and can be developed, deployed, and scaled on its own.
For most modern IoT systems, a microservices approach isn’t just a preference; it’s a necessity. It gives you the flexibility to scale individual components, push updates without downtime, and manage the complexity of a massive, distributed network.
This modularity is everything. If your data ingestion service suddenly gets slammed with traffic, you can scale just that one component without touching anything else. This doesn't just improve reliability; it makes your development process faster. Different teams can work on different services in parallel, slashing your time to market.
Managing these complex, containerized environments is a discipline in itself. For leaders navigating this shift, exploring expert guidance like Kubernetes consulting services can show you how to streamline the adoption of cloud-native tech.
Edge vs Cloud Computing
Another critical choice is deciding where data processing happens. This is a balancing act between the need for real-time responsiveness and the raw power of large-scale analytics.
Picture an autonomous vehicle. The system that spots an obstacle and slams on the brakes is a perfect example of edge computing. That decision has to be made instantly, right there on the device. Waiting for data to travel to a distant server isn't an option when safety is on the line.
At the same time, all the long-term performance data—engine temperature, tire pressure, route history—gets sent to the cloud for analysis. This is cloud computing, where huge datasets can be stored and processed to spot trends, predict maintenance, and improve the entire fleet’s performance.
A truly successful IoT architecture uses both:
Edge Computing for immediate, low-latency processing and real-time decision-making.
Cloud Computing for heavy-duty data analysis, massive storage, and centralized management.
A core piece of any strong IoT system is moving massive volumes of data efficiently. To get a better handle on this, it’s worth understanding how to build a data pipeline to manage these critical information flows.
Building an architecture that can stand the test of time requires a deep bench of expertise in both cloud systems and embedded engineering. Finding talent with this rare mix of skills is a huge challenge. TekRecruiter specializes in sourcing the top 1% of engineers who can design and build the complex, scalable IoT systems your business needs to win.
Choosing the Right IoT Technology Stack
Picking the right technology for your IoT application is a lot like building a high-performance car from scratch. You wouldn’t put a lawnmower engine in a race car, right? The components you choose—the hardware, the communication protocols, the cloud services—will define what your system can do, how reliable it is, and how painful it will be to maintain down the road.
This isn’t about chasing the “best” tools. It’s about assembling the right combination for your specific goals, starting at the very edge of your network: the physical devices themselves.
Selecting Device Hardware and Protocols
The hardware is where your system makes contact with the real world. Every choice here is a careful balancing act between cost, how much power it drains, and how much thinking it can do on its own.
Prototyping Powerhouses (Raspberry Pi): For a project that needs to do some heavy lifting on-site—like a smart security camera running machine learning models to spot intruders—a single-board computer like a Raspberry Pi is perfect. It runs a full Linux environment, making it feel more like a tiny server than a limited gadget.
Low-Power Workhorses (Arduino, ESP32): What if you just need a remote sensor to report the temperature once an hour for the next three years on a single battery? That’s where microcontrollers shine. An Arduino or ESP32 is built for simple, repetitive tasks where sipping power is the name of the game.
Once the hardware is sorted, you have to decide how it’s going to phone home. This is where communication protocols come in—they’re the language your devices use to send data back to the mothership.
The explosive growth of the Industrial IoT (IIoT) has made MQTT the go-to protocol for many applications. Its lightweight, publish-subscribe model is perfect for sending data reliably from thousands of remote sensors across manufacturing, energy, and automation sectors.
Two protocols dominate the IoT space: MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) and CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol). MQTT was born for spotty, low-bandwidth networks, making it incredibly efficient for battery-powered devices that can't afford to waste energy. CoAP, on the other hand, is built to work over UDP and gives you a simple request/response model, almost like a lightweight version of HTTP, but without all the baggage.
Comparing the Major IoT Cloud Platforms
If your devices are the hands and feet of your system, the cloud is the brain. This is where all the data gets sent, processed, analyzed, and managed at a massive scale. The "big three" cloud providers—Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP)—all have incredibly powerful IoT suites.
The choice often comes down to what your team already knows, what your company already uses, and what your project truly needs.
These platforms do a lot more than just store data. They provide the critical APIs and services that bridge the gap between your army of devices and your user-facing applications. If you want to really nail those connections, digging into API development best practices is a must-do for any serious engineering team.
So, how do the big three stack up for IoT development? Let's take a quick look.
Comparison of Major IoT Cloud Platforms
Each of the major cloud providers offers a compelling suite of tools for IoT, but they each have their own strengths and are better suited for different types of projects.
Feature | AWS IoT | Azure IoT Hub | Google Cloud IoT |
|---|---|---|---|
Core Function | Securely connects devices and routes messages to other AWS services. | Acts as a central message hub for bi-directional communication with devices. | Provides secure device connection and management services. |
Device Management | Excellent, with features like Device Shadow, Fleet Indexing, and Secure Tunneling. | Robust, offering device twins, direct methods, and automatic device provisioning. | Strong, with a focus on device registry, metadata, and state reporting. |
Best-Fit Scenario | Teams already heavily invested in the AWS ecosystem, seeking deep integration with services like Lambda, S3, and Kinesis. | Enterprises with a strong Microsoft footprint (e.g., using Office 365, Dynamics) or those building complex industrial IoT solutions. | Projects requiring powerful data analytics and machine learning integration with tools like BigQuery and Vertex AI. |
Ultimately, the best platform is the one that fits your business goals like a glove. AWS brings an unmatched breadth of services, Azure offers seamless integration for enterprises, and GCP is the undisputed champion for data-heavy, AI-driven applications.
Of course, putting together a world-class tech stack is only half the battle. You also need a team with the rare blend of skills to build, deploy, and manage it all. Finding engineers who are just as comfortable with embedded systems as they are with cloud architecture is a massive challenge.
TekRecruiter bridges that gap, connecting you with the top 1% of engineers who can take your chosen tech stack and turn it into a market-leading IoT solution.
Mastering the IoT Development Lifecycle
Taking a great idea and turning it into a real, market-ready IoT product is a completely different beast than a standard software project. The IoT application development lifecycle is a complex dance between physical hardware and cloud-based software, where a single bug in one can cripple the other. If you don't nail this process, you're just building a collection of incompatible parts, not a functional product.
You're essentially managing two separate worlds. One team is deep in the weeds of firmware, wrestling with a microcontroller's power consumption and memory limits. At the same time, another team is building scalable microservices in the cloud. A disciplined, agile, and repeatable lifecycle is the only way to make sure these parallel streams actually merge into something that works.
This diagram shows the basic flow, from the physical hardware all the way up to the cloud.
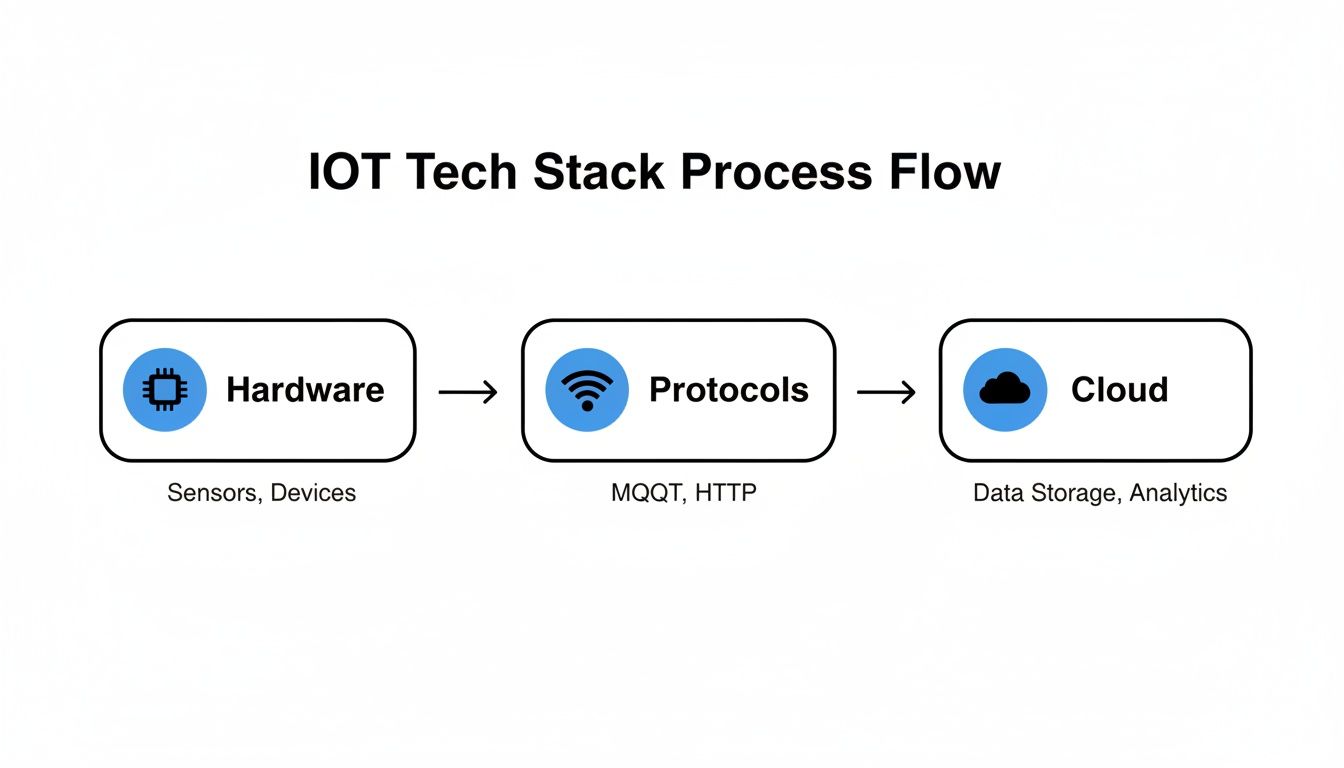
As you can see, each layer depends heavily on the one below it. This is why a development process that treats hardware, firmware, and cloud software as a unified whole isn't just a "nice-to-have"—it's critical.
Stages of IoT Development
The journey typically moves through several distinct, yet overlapping, phases. Each one brings its own unique set of challenges that demand a mix of hardware engineering, embedded software development, and modern cloud practices.
Hardware Prototyping: This is where it all begins. You're selecting microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators to create a physical proof-of-concept. This isn't just about function; it has to meet the product's real-world environmental requirements, too.
Firmware Development: With the hardware locked in, engineers write the low-level software that lives on the device itself. This is the code that reads sensors, manages connectivity, and actually executes commands.
Cloud Integration: The device has to talk to the cloud—securely. This stage is all about setting up device authentication, building data ingestion pipelines, and figuring out storage.
Application Development: Finally, you build the user-facing web or mobile app. This is how your customers will monitor, manage, and interact with all those connected devices out in the field.
CI/CD for the Internet of Things
A modern Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline is your secret weapon for managing all this complexity. But an IoT pipeline isn't your standard web app deployment. Not even close.
In IoT, "deployment" doesn't just mean pushing code to a server. It means safely updating the firmware on thousands or even millions of physical devices scattered across the globe, without bricking them.
One of the biggest hurdles is mastering Over-the-Air (OTA) updates. A botched OTA update can turn a customer's expensive gadget into a paperweight, instantly. Your CI/CD pipeline absolutely must include hardcore testing and phased rollouts to ensure every update is both reliable and secure. Automating tests across a huge, diverse fleet of physical devices is another massive challenge, often requiring a dedicated hardware lab or sophisticated simulation environments.
On top of that, a comprehensive approach to quality assurance is completely non-negotiable. For a solid primer on this, check out our guide that breaks down what quality assurance in software development actually means—the core principles apply here, but with much higher stakes. Security checks have to be baked in at every single stage, from static code analysis on the firmware to penetration testing on your cloud infrastructure.
Navigating the IoT development lifecycle successfully requires a team with a rare blend of skills—people who are fluent in hardware, embedded systems, and cloud-native engineering. Finding and keeping that kind of talent is often the biggest bottleneck for companies trying to innovate. TekRecruiter specializes in connecting companies with the top 1% of engineers who have this exact cross-disciplinary expertise. We help you deploy the elite talent you need, anywhere in the world, to turn complex hardware-software challenges into market-leading products.
Implementing Rock-Solid IoT Security

Let's be blunt: in IoT application development, security isn't a feature you add at the end. It’s the foundation. If you treat it like an afterthought, you're building on sand. Every connected sensor, every industrial controller—each one is a potential doorway for attackers.
A single weak point can compromise the entire system. Without a robust, multi-layered defense, you aren’t just risking data. You’re putting your operations, customer trust, and your entire brand on the line. This demands a security-first mindset, weaving defensive measures into every stage of the lifecycle, not just bolting them on before launch.
Fortifying Devices at the Edge
Your security posture starts right at the hardware. Hardening these endpoints is your first and most critical line of defense against both physical tampering and remote attacks. It's where the rubber meets the road.
Two practices are non-negotiable here:
Secure Boot: Think of this as a bouncer for your device's firmware. From the moment it powers on, Secure Boot creates a chain of trust, cryptographically verifying that the code it’s loading is authentic and hasn't been hijacked. Unauthorized code simply doesn't get to run.
Data Encryption: Any sensitive data—whether it's stored on the device (at rest) or being sent over the network (in transit)—must be encrypted. End of story. We're talking standards like AES for storage and TLS/DTLS for communication.
Security isn't a one-and-done task; it’s a continuous process. You have to assume vulnerabilities will be found eventually. That’s why a secure over-the-air (OTA) update mechanism is one of the most powerful security tools in your arsenal.
The sheer scale of the market makes this critical. The global IoT market is on track to hit $875 billion in 2025. Industries like transportation and utilities already have over 100 million devices in the field. That’s a massive attack surface.
Securing Network and Cloud Communications
Once data leaves the device, it hits the network—another prime target. Your application has to enforce strict protocols to shield that data as it travels between the device, gateways, and the cloud.
This means using transport layer security protocols like TLS (for TCP) and DTLS (for UDP) to create encrypted, private tunnels for all communication. Just as important, every single device must be uniquely identified and authenticated before it’s even allowed to connect to your network, typically using digital certificates or secure tokens.
Navigating Data Privacy and Compliance
Beyond the technical nuts and bolts, you have to tackle data privacy and regulatory compliance. Rules like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California have real teeth, dictating exactly how personal data can be collected, stored, and managed.
Designing your system for compliance from day one isn't just good practice; it's essential. This involves data minimization—only collecting what you absolutely need—and giving users clear, direct control over their information. To get a wider perspective, it's worth reviewing some foundational software development security best practices.
Building a truly rock-solid IoT security strategy requires a rare blend of expertise in embedded systems, network security, and cloud architecture. Finding engineers with that specific skill set is a huge challenge for most companies. TekRecruiter specializes in connecting innovators with the top 1% of security and IoT engineers, giving you the elite talent needed to build a resilient and trustworthy system from the ground up.
Build Your Elite IoT Team with TekRecruiter
Let's be blunt: even the most brilliant strategy for IoT application development is just a concept on a whiteboard without the right people to build it. Your technical blueprints for architecture, security, and lifecycle management are crucial, but execution is everything. This is where theory hits reality, and where most ambitious IoT projects die on the vine.
Building a successful IoT product demands a rare mix of highly specialized skills. It’s not enough to find a great cloud developer or a talented firmware engineer. You need people who can operate fluently across the entire hardware-software divide, and those experts are in ridiculously high demand.
The Specialized Roles Your IoT Project Can't Live Without
A high-performing IoT team is a carefully assembled unit of diverse specialists. Think of it like a special ops team—each role is a critical piece of the puzzle, and a gap in any one area creates bottlenecks or, worse, vulnerabilities in your product.
Embedded Systems Engineers: These are the experts writing the low-level code that runs right on your physical devices. They manage everything from sensor data collection to squeezing every last drop of power out of the battery.
Cloud Architects: They design the scalable, resilient cloud backend that has to ingest, process, and make sense of the massive data streams flooding in from your device fleet.
Data Scientists & AI Engineers: This team turns all that raw data into actual business value. They build the machine learning models that enable killer features like predictive maintenance or real-time anomaly detection.
Security Specialists: From hardening the device itself to encrypting network traffic, they build the multi-layered defenses needed to protect your system and your customers' trust.
Assembling this roster is a huge undertaking. For a deeper look into just how complex sourcing top-tier technical talent can be, check out our ultimate guide to recruiting and hiring software engineers.
The greatest challenge in IoT isn't just the technology; it's finding the rare combination of talent with deep expertise in hardware, firmware, cloud infrastructure, and data science—all in one cohesive team.
This is where TekRecruiter gives you a decisive edge. We get it. Your project's success hinges on having access to elite engineering talent. As a premier technology staffing and recruiting firm, we specialize in one thing: connecting innovative companies with the top 1% of engineers in IoT, AI, and cloud technologies.
Our tailored staffing solutions and AI Engineer firm capabilities mean you can deploy world-class talent precisely where you need it, anywhere in the world. Whether you need to augment your existing team, hire key players directly, or outsource a complex AI component, we provide the people who can accelerate your development and lock in a lasting competitive advantage.
Let's build the elite team that turns your IoT vision into a market-leading reality.
A Few Common IoT Questions We Hear All the Time
When you're mapping out an IoT project, especially your first big one, a handful of questions always seem to surface. Getting straight answers to these is the difference between a confident strategy and a series of costly mistakes down the line. We've heard these from countless CTOs and engineering leaders, so let's tackle them head-on.
Answering these questions is a great start, but the real test is turning that knowledge into a product that works in the wild.
What Is the Single Biggest Challenge in IoT Application Development?
Nine times out of ten, it’s security. It’s not just a feature; it’s the foundation. When you have thousands—or potentially millions—of devices connected to the internet, every single one is a potential backdoor for an attacker. Building a truly comprehensive security strategy is a massive undertaking.
You can't just bolt it on at the end. It demands a defense-in-depth approach from day one:
Device-Level Hardening: Think of this as locking the front door. You need features like secure boot to guarantee only your trusted firmware can ever run on the device.
End-to-End Encryption: Data needs to be protected everywhere—at rest on the device and in transit across the network. No exceptions.
Secure Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: You will find vulnerabilities after launch. A rock-solid OTA system is non-negotiable for patching them quickly without turning your devices into expensive bricks.
How Do I Choose Between MQTT and HTTP for My Project?
This decision really comes down to what your devices can handle and how reliable your network is.
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) was built for the realities of IoT. It’s incredibly lightweight and efficient, which makes it the go-to for small, battery-powered sensors that might be operating on shaky cellular or Wi-Fi connections. It sips power and bandwidth.
On the other hand, HTTP/HTTPS is the devil everyone knows. It’s familiar and easier for many web developers to get started with, but it's "chatty." Its verbose nature can drain the battery on a small sensor in no time. For most serious IoT applications, MQTT has become the de facto standard for a good reason.
What’s the Real Role of AI and Machine Learning in IoT?
This is where things get interesting. AI and Machine Learning (ML) are what elevate an IoT system from a simple data firehose into a source of genuine business intelligence. Instead of just passively collecting sensor readings, AI/ML models can get to work analyzing that data to find patterns and make decisions.
AI and ML are the engines that turn IoT data into proactive, intelligent action. They enable systems to predict failures, detect threats, and optimize operations automatically, creating immense value beyond simple monitoring.
This isn’t just theoretical. We're talking about predictive maintenance that spots when a factory machine will fail before it breaks down, saving a fortune in downtime. Or anomaly detection that flags a security breach the second it happens. Or a smart building that adjusts its own energy use based on who’s actually inside. That’s the power of AI in IoT.
Solving these challenges takes more than the right tech stack—it requires elite engineers who have done it before. As a leading technology staffing, recruiting, and AI Engineer firm, TekRecruiter allows innovative companies to deploy the top 1% of engineers, anywhere in the world. Let us help you build the world-class team you need to bring your IoT vision to life. Find out how we can help at TekRecruiter.
Comments